GST Software

What is GST and How its Work ?
We build relations then business.
Goods & Services Tax is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that will be levied on every value addition. GST is one indirect tax for the whole nation, which will make India one unified common market.
GST is a single tax on the supply of goods and services, right from the manufacturer to the consumer. Credits of input taxes paid at each stage will be available in the subsequent stage of value addition, which makes GST essentially a tax only on value addition at each stage. The final consumer will thus bear only the GST charged by the last dealer in the supply chain, with set-off benefits at all the previous stages.
Invoicing Under GST
GST defines a transaction as ‘Supply’ when there is a transfer, exchange, rental, lease, barter, disposal or license of goods or services. Whenever a transaction takes place, a tax invoice has to be issued depending on the occurrence of any such event or within a prescribed time limit. Hence, every taxpayer registered under the GST network shall be required to issue a tax invoice for the supply of goods or services.
The invoice contains S.No, details of product such as product name, description, quantity, etc along with details of supplier, purchaser, tax charged and other particulars such as discounts, terms of sale etc.
FAQ's for better understanding in GST
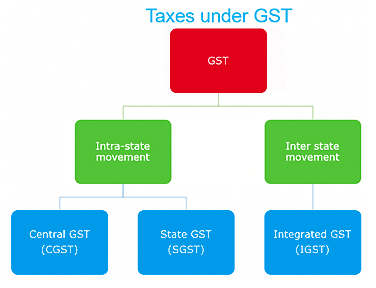
The GST too needs to have clear provisions on what areas the centre and the state are allowed to collect revenue from taxation to prevent an overlapping.
The Central GST or CGST is the areas where the centre has the powers and State GST where the State has taxation capabilities. The IGST or Integrated GST is for movement of goods within the states of the Indian union. This will be collected by the union however will be transferred over to the states. Thus it is essential that if and when the GST comes out it is rolled over in the entire nation simultaneously.
Goods & Service Tax or GST will be levied on goods and services. It will replace all the various taxes and bring them under one umbrella to make compliance easier. It will replace the following taxes:
(i) Taxes currently levied and collected by the Centre:
- Central Excise duty
- Additional Duties of Customs (commonly known as CVD)
- Special Additional Duty of Customs (SAD)
- Service Tax
AND
(ii) Taxes currently levied and collected by the State:
- State VAT
- Central Sales Tax
- Entertainment and Amusement Tax (except when levied by the local bodies)
- Taxes on lotteries, betting and gambling
Why are we getting 3 taxes -SGST, CGST, IGST?
India is a federal country where both the Centre and the States have been assigned the powers to levy and collect taxes. Both the levels of Government have distinct responsibilities to perform, as per the Constitution, for which they need to raise resources. A dual GST will, therefore, be keeping with the Constitutional requirement of fiscal federalism.
The Centre and States will be simultaneously levying GST.
3 taxes will be implemented to help tax-payers to take credit against each other thus ensuring “One nation one tax”.
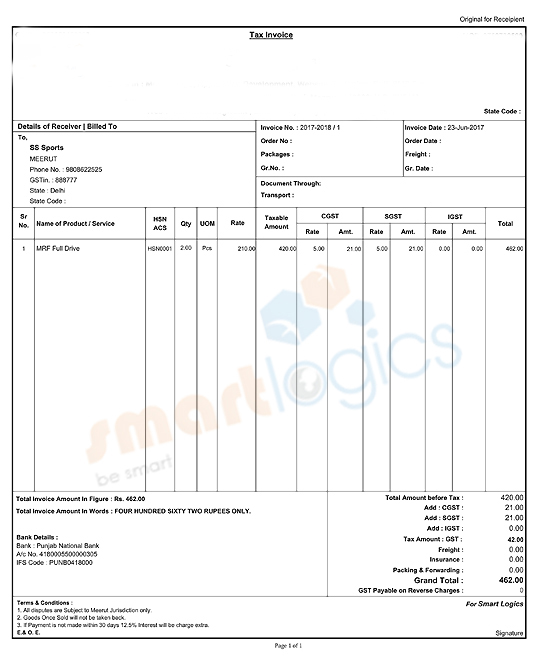
Tax Invoice
When a registered taxable person supplies taxable goods or services, a tax invoice is issued.
Bill of Supply
Bill of Supply is to be issued by a registered supplier in the following cases:
- Supply of exempted goods or services
- Supplier is paying tax under composition scheme
Tax invoice is generally issued to charge the tax and pass on the credit. In GST there are some instances where the supplier is not allowed to charge any tax and hence a Tax invoice can’t be issued instead another document called Bill of Supply is issued.
- Name, address and the GSTIN of the supplier
- The nature of invoice (tax invoice, supplementary invoice or revised invoice)
- Invoice number (this shall be a consecutive alpha-numeric or numeric series, specific for a financial year)
- Date of Invoice
- Name, address and the GSTIN of the recipient
- Where the value of the goods exceeds Rupees Fifty Thousand and the recipient is an unregistered person, then name and address of such recipient and the delivery address of the consignment.
- Description of the goods or services
- HSN code of the goods or the Accounting Code of the Services
- Quantity of the goods or services
- Total value of the goods or services
- Rate of Tax on each item
- Tax amount charged, on account of CGST, IGST, and SGST to be shown separately under different columns
- Name of the supplying State and the place of supply
- Place of delivery
- A statement mentioning whether reverse charge is applicable or not
- Trade Discounts not forming part of value of the goods, if any
- Signature in physical form or Digital Signature of the supplier or an authorized person, duly certifying the invoice In addition to the above particulars, an export invoice shall include the following.
- A mandatory statement mentioning these specific words – “SUPPLY MEANT FOR EXPORT ON PAYMENT OF IGST” or “SUPPLY MEANT FOR EXPORT UNDER BOND WITHOUT PAYMENT OF IGST.”
- Country of destination
- Delivery address
- The Number and date of application of form for removal, i.e. Form ARE-1 Likewise, when an Input Service Distributor issues the invoice, then “Amount of credit distributed” shall also be added to the invoice instead of the rate and value of the goods or services. If you are a Goods Transport Agency, you are a critical link in the supply chain and has to include the following in your invoice.
- Name and address of the consignor and the consignee
- Registered Vehicle number
- Gross weight of the consignment
- Place of Origin
- Destination
- GSTIN of the person liable to pay tax The transporter does not require to the Duplicate copy of the Invoice. Instead, they can opt for Invoice Reference Number, which can be generated by the supplier by uploading the tax invoice onto the GST Portal. The portal shall generate a number that is valid for 30 days from such date. Apart from the tax invoice, other important documents include Supplementary Invoice, Revised Invoice, Debit or Credit Notes, and Bill of Supply. Let us discuss each one in details.
GST Invoice Format
For supply of goods, three copies of the invoice are required – Original, Duplicate, and Triplicate.
Original invoice: The original invoice is issued to the receiver, and is marked as ‘Original for recipient’.
Duplicate copy: The duplicate copy is issued to the transporter, and is marked as ‘Duplicate for transporter’. This is not required if the supplier has obtained an invoice reference number. The Invoice reference number is given to a supplier when he uploads a tax invoice issued by him in the GST portal. It is valid for 30 days from the date of upload of invoice.
Triplicate copy: This copy is retained by the supplier, and is marked as ‘Triplicate for supplier’.
Let us assume that the GST is set at 20%. Suppose that the manufacturing cost of a Product A is 100 and assuming a GST of 20% the total amount is Rs. 120. The next step of taxation would be when the Product is sold to consumers, let’s say at a price of 150. So the GST will charge another 20% on just the difference of Rs. 150 and Rs. 120 i.e. only 20% on Rs. 30 which is equal to Rs. 6. So the final price is Rs. 150 + Rs. 6. Unlike the case of petrol pricing there is no tax on a tax now. This eliminates the cascading effect of taxes which is very prevalent in our economy and has been simplified to an elemental level in the example.
Since the GST will be applied at every step of value creation it will be very difficult for black money owners to participate anywhere in the value chain with the GST without accounting for all other transactions. The GST is estimated to provide an immediate boost of 0.9% – 1.4% of the GDP.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) will be levied at multiple rates ranging from 0 per cent to 28 per cent. GST Council finalised a four-tier GST tax structure of 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%, with lower rates for essential items and the highest for luxury and de-merits goods that would also attract an additional cess. Service Tax will go up from 15% to 18%. The services being taxed at lower rates, owing to the provision of abatement, such as train tickets, will fall in the lower slabs. In order to control inflation, essential items including food, which presently constitute roughly half of the consumer inflation basket, will be taxed at zero rate. The lowest rate of 5% would be for common use items. There would be two standard rates of 12 per cent and 18 per cent, which would fall on the bulk of the goods and services. This includes fast-moving consumer goods.
Highest tax slab will be applicable to items which are currently taxed at 30-31% (excise duty plus VAT). Ultra luxuries, demerit and sin goods (like tobacco and aerated drinks), will attract a cess for a period of five years on top of the 28 per cent GST. The collection from this cess as well as that of the clean energy cess would create a revenue pool which would be used for compensating states for any loss of revenue during the first five years of implementation of GST.
Finance minister said that the cess would be lapsable after five years. The structure to agreed is a compromise to accommodate demand for highest tax rate of 40% by states like Kerala. While the Centre proposed to levy a 4% GST on gold but the final decision on this was put off. During a press conference, finance minister Mr. Jaitley said, “GST rate on gold will be finalised after the fitting to the approved rates structure of all items is completed and there is some idea of revenue projections”.
The principle for determining the rate on each item will be to levy and collect the GST at the rate slab closest to the current tax incidence on it. The GST will subsume the multitude of cesses currently in place, including the Swachh Bharat Cess, the Krishi Kalyan Cess and the Education Cess. Only the Clean Environment Cess is being retained, revenues from which will also fund the compensations.
HSN or HS (Harmonised Commodity Description and Coding System) is a multipurpose international product nomenclature developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO).
Why is it required?
Every business is required to declare list of goods they are dealing into. This declaration is required along with the HSN code of such commodity. System will automatically pick tax rate under GST regime based on these HSN codes. Thus it is of utmost importance to mention correct HSN codes at the time of enrollment or registration under GST
Where original tax invoice has been issued and taxable value/GST tax amount in the invoice exceeds/falls shorter than the actual taxable value/tax amount, in such cases the supplier can issue debit/credit note. Under this section we will cover the cases where debit notes/credit notes can be issued, the format, particulars to be included etc. We will also understand the difference between a revised invoice and a supplementary invoice.
The GST will fuel inflation for the short term. The GST rate starts at 5% and 18% taxation services such as restaurants, movies etc. are bound to increase prices. Another problem with the GST that many pundits feel is not including liquor and petroleum under GST’s ambit. These are major revenue sources for the government and experts feel this is being done due to a few crony capitalists who need some time to funnel away their black money as the GST promises to widen the tax paying population.